The blockchain revolution has made it possible for communities to organize, fund, and govern themselves without the need for centralized intermediaries. This marks the start of a new era of decentralized government. This patch is all about Decentralized Autonomous Organizations, or DAOs. They are online co-ops that use smart contracts to make decisions, vote, and handle money. As Web3 has grown up, DAOs have become the most crucial aspects of decentralized finance (DeFi), NFT ecosystems, open-source development, and communal investment vehicles. This long piece talks about the five finest DAOs that are making Web3 better. We discuss about where they come from, how they function, how their tokens work, how people use them, what new things they are doing, and what challenges they have.
1. MakerDAO: The first stablecoin that isn’t run by one individual What it is and where it originated from
In late 2017, the Maker Foundation created MakerDAO. The idea was to build a decentralized stablecoin called DAI that is backed by collateral and whose value stays tied to the US dollar through over-collateralization and automated liquidation processes. The goal is to make it secure and stable to borrow money on Ethereum without getting blocked.
1.2 How the Management Model Works Token: People that own MKR
Voting Methods: Snapshot and on-chain voting modules let people submit modifications to risk parameters, contribute collateral, and make the system better.
Quorum and involvement: The MakerDAO forum uses active stake-weighted voting and off-chain discussion to make sure everyone can see what’s going on. This is part of a dynamic quorum approach that encourages involvement.
1.3 Keeping the Treasury DAI and Tokenomics Fees Stable: They get paid in MKR, which is then burned, which makes MKR worth less.
Emergency Shutdown: A safety mechanism that lets the community turn off the system in case of a calamity and return collateral to DAI holders.
1.4 Important Uses
Money sent over the world: You can send money anywhere in the world with DAI for a minimal fee and without being blocked.
DAI is an example of DeFi collateral because you can use it as collateral on sites that lend money, including Aave and Compound.
1.5 New Ideas and Growth
Multiple Collateral DAI, or MCD This feature was added in 2019, and now you can utilize several types of collateral, including as ETH, BAT, and USDC.
Real-World Assets (RWA): agreements to add tokenized real-world collateral into the mix, integrating TradFi and DeFi.
1.6 Issues and a look forward
Regulatory Scrutiny: New laws governing stablecoins could impact how people find collateral.
Governance participation: It’s still vitally crucial that everyone has a say.
The website is makerdao.com.
You may find this information in the MakerDAO guide on CoinDesk (coindesk.com/makerdao-guide).
2. Uniswap DAO: Making market making that happens automatically more fair
2.1 What it is and where it comes from: Uniswap v3 and Uniswap DAO were both made in May 2021. The idea was to offer the community greater control over how things are run through the UNI token and make automated market makers (AMMs) less centralized. The point is to enable users trade tokens and add liquidity without having to ask first.
2.2 The Model’s Rules of the Game: UNI
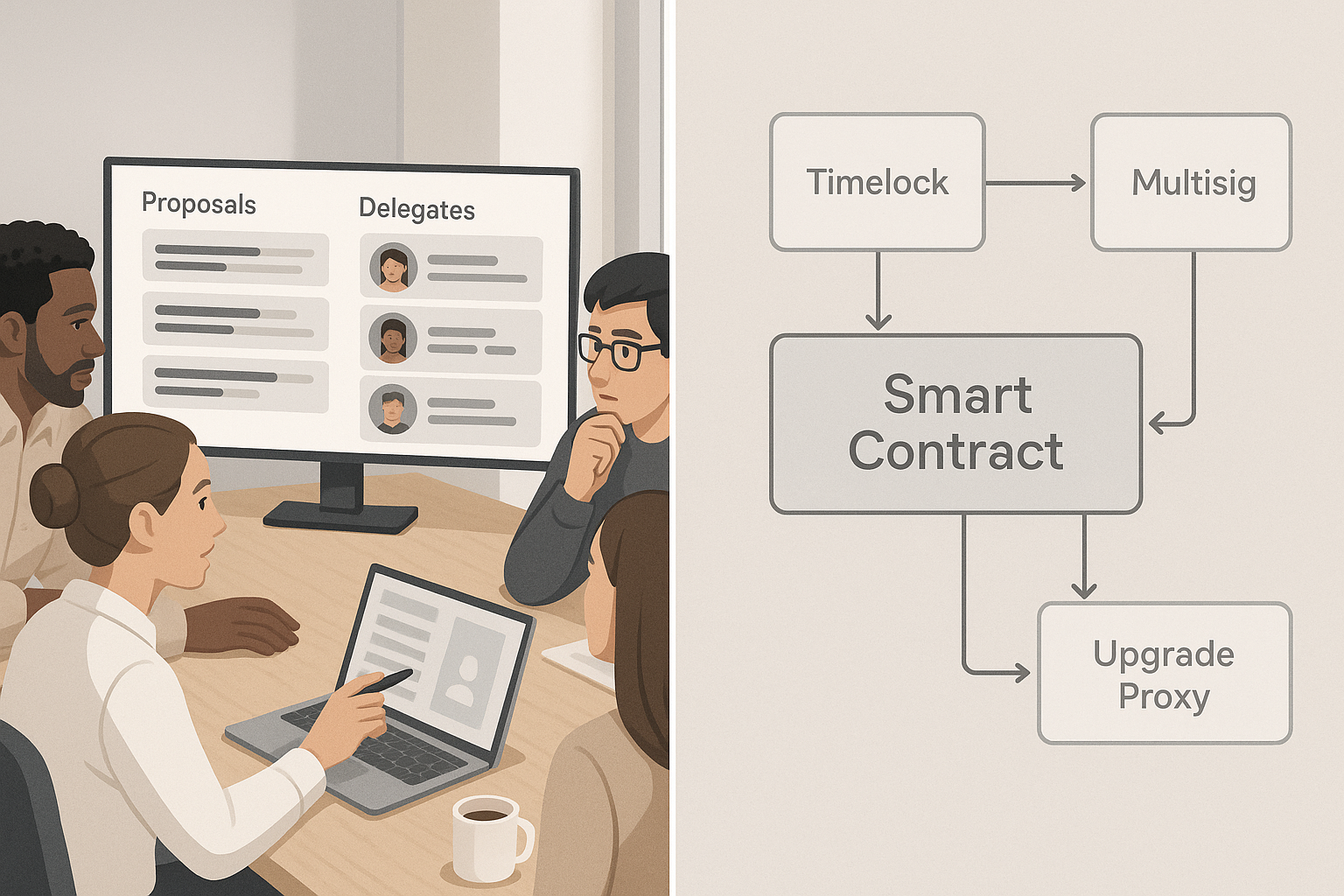
You can submit proposals on-chain with the Governor Bravo contract. People who hold tokens can give their votes to delegates to indicate that they know what they’re talking about.
Timelock: Proposals that have been approved will be put on hold for two days so that the community can see them.
2.3 Tokenomics and Rewards People that add liquidity to pools, especially new ones, gain UNI benefits for doing so.
Community Treasury: A portion of the protocol fees goes to the DAO treasury, which can be utilized for grants, ecosystem growth, and forming strategic collaborations.
2.4 Important Examples of Use
You don’t have to get anyone’s permission to list any pair of ERC-20 tokens.
Custom Fee Tiers: Uniswap v3 included programmable fee tiers that help you make the most out of your money when you trade different sorts of goods.
2.5 New Ideas and Changes
Concentrated Liquidity: When liquidity providers put a lot of money into a small number of price ranges, it makes capital work better.
NFTs have liquidity positions that are not interchangeable. This means that they can be used with NFT marketplaces and DeFi tools.
2.6 Issues and the Future
People are looking into Flashbots integrations and batch auctions as ways to decrease the dangers of MEV and front-running.
Cross-Chain Expansion involves shifting Uniswap liquidity from one Layer 2 to another or to a different chain.
You can get additional information at uniswap.org.
This originated from the Uniswap v3 whitepaper at uniswap.org/whitepaper-v3.pdf.
3. Aave DAO: financing that is safe, open, and highly fast
3.1 Where it comes from and what it intends to do
In 2017, Aave DAO was called ETHLend. In 2018, it became known as Aave. People can borrow and lend items without asking for permission or trusting anyone. The DAO is in responsible of monitoring risk, community-led projects, and upgrading protocols.
3.2 How to Use AAVE to Keep Track of Your Governance Token
In the Governance Portal, you can send signals with Snapshot. You can also vote on-chain with Aave’s governance contracts.
Safety Module: People in the community stake AAVE to keep the protocol from losing money and gain rewards.
3.3 Tokenomics and the Ecosystem’s Growth
The asset that is being loaned pays the fees, and some of that money goes to people who stake AAVE.
Safety Incentives: AAVE stakers take on risk and obtain protocol fees and rewards for emissions.
3.4 Important Use Cases
Flash Loans are fast loans that don’t need any collateral. You can utilize them for self-liquidation, swapping collateral, and arbitrage.
Debt Tokens automatically earn interest in users’ wallets.
3.5 New concepts and links
As long as they meet KYC and AML standards, institutions can utilize Aave Arc, which is a kind of DeFi.
You can move money between chains using portals to Polygon, Avalanche, and other chains.
3.6 Issues and the Future: Smart contracts include risks, thus regular audits and formal inspections are highly important.
Regulatory Adaptation: Figuring out how to be decentralized while still following the rules.
The site is called Aave.com.
The Aave protocol’s documentation (docs.aave.com)
4. Aragon DAO: Setting up the legal framework for Web3 4.1 Where it comes from and what it is
Luis Cuende and Jorge Izquierdo launched Aragon DAO in 2016. It offers easy-to-use interfaces and plug-and-play governance components that make it straightforward to set up and run DAOs. The idea is to help businesses all across the world run successfully without needing aid from anyone else.
4.2 ANT is the Model’s Control Governance Token.
Aragon Court is a means to adjudicate disputes on the blockchain by having people stake ANJ tokens.
DAOs can pick from a number of governance styles, such as voting, token-weighted, or reputation-based.
4.3 Tokenomics and Ecosystem: You need to stake ANT to build a DAO and vote on Aragon Improvement Proposals (AIPs).
Aragon Network Fee: A little amount of ANT that goes to network services, development, and funding.
4.4 Business and Community Use Cases: Aragon used open-source funding to buy tools for the ecosystem, such as state channels and DAO tools.
In the actual world, there are groups like decentralized grant programs and investment clubs.
4.5 New ideas and noteworthy things that happened
AragonOS and Aragon Court v2: jurors get more modularity and prizes.
You don’t have to pay gas fees to vote in governance if you use Snapshot Integration.
4.6 Problems and a Look Ahead Juror Participation: Making sure that jurors are honest and know what they’re talking about.
Scalability implies making sure that big DAOs with a lot of members can work without problems.
You can find the site at www.aragon.org.
The Aragon whitepaper (aragon.org/aragon-whitepaper-2020.pdf) is the source.
5. Gitcoin DAO: Giving money to public goods and free software
5.1 What it is and how it got here
Gitcoin DAO launched in 2017 as a mechanism to connect open-source grants and bounties. It was a very different DAO by 2022. Its purpose is to leverage quadratic funding to pay for things that are useful for society, such as initiatives, research, and open-source code.
5.2 GTC: A token for keeping track of model governance
Quadratic Voting: This system gives money based on the square root of the amount supplied. This indicates that little presents have the most impact.
Guilds and SubDAOs are groups that do certain tasks and can suggest projects and hand out cash.
5.3 What is tokenomics and how to make money
GTC Staking: This provides protocols a motivation to work together and helps settle differences in quadratic funding cycles.
Grants Rounds: Gitcoin Grants rounds happen all the time, and they are paid for by sponsors, community matching, and protocol revenue.
5.4 How Public Goods Affect Open-Source Development: Developers and researchers have gotten more than $50 million since the project began.
Web3 Education: Paying for classes, hackathons, and other ways to study all across the world.
5.5 New alliances and ideas
The Decentralized Grants Protocol (DGP) makes quadratic funding work the same way across all ecosystems.
Corporate Matching: The Polygon Foundation, ConsenSys, and other Web3 groups are working together on this.
5.6 Issues and what to look forward to in the future
Identity solutions like Proof of Humanity can assist thwart Sybil assaults.
Finding strategies to create money that don’t depend on grant cycles.
The address of the site is gitcoin.co.
The Gitcoin Blog talks about the migration to DAO (blog.gitcoin.co/gitcoin-dao)
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
How does a DAO differ from other groups?
A Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) is a group that runs on the blockchain and is run by smart contracts and people who possess tokens. No one is in command. People in charge of a firm usually make the decisions. This system makes decisions using on-chain voting instead.
How do I become a member of a DAO?
You normally need to get the DAO’s governance token, like MKR or UNI, then either stake or delegate your votes to vote. Some DAOs additionally require KYC to vote or join on-chain subDAOs.
Q3: Is it safe to use DAOs?
Even while smart contract audits and multisig protections help, DAOs are still at risk for things like flash loan assaults, governance manipulation, and regulatory uncertainty. Before you get involved, always do your research.
Q4: How do DAOs make money?
DAOs create money by charging protocol costs (like trading fees, interest, and stability fees), issuing tokens (like emission schedules), and collecting service fees (like network fees and transaction fees) that go into the treasury.
What does “quadratic funding” mean?
A mechanism for people in a community to pay for a project where the amount of money it gets depends on how many people provide money. This means that smaller donations have a bigger effect and that grants are paid out in a more fair way.
In short, DAOs are the next big thing for running enterprises. Not businesses or governments run them; people who live there do. They are open and pay for themselves. These five DAOs show that Web3 can use decentralized governance in many different ways. For instance, MakerDAO’s new mechanism for stablecoins and Gitcoin’s new approach to pay for public goods.
As blockchain technology and rules change, DAOs will keep making their models better and safer. They will also move into new fields like art, gaming, and institutional finance. You need to know what DAOs are if you want to be able to go around in the decentralized future, whether you’re a developer, investor, or fan.
References
- MakerDAO Official Site. https://makerdao.com
- CoinDesk – MakerDAO Guide. https://www.coindesk.com/learn/makerdao-explained
- Uniswap Whitepaper v3. https://uniswap.org/whitepaper-v3.pdf
- Uniswap Official Site. https://uniswap.org
- Aave Protocol Docs. https://docs.aave.com
- Aave Official Site. https://aave.com
- Aragon Whitepaper. https://aragon.org/aragon-whitepaper-2020.pdf
- Aragon Official Site. https://aragon.org
- Gitcoin Blog – DAO Transition. https://blog.gitcoin.co/gitcoin-dao
- Gitcoin Official Site. https://gitcoin.co










1 Comment