If you’re building in AR/VR, the real growth is increasingly outside games. This guide maps the AR/VR resurgence to proven, repeatable use cases where startups can create value fast, sell into budgets that already exist, and scale beyond pilots. In one line: AR (overlaying digital information on the real world) and VR (fully simulated environments) become “spatial interfaces” that compress error, time, and travel. You’ll find practical plays, buyer expectations, KPIs, and guardrails so you can ship a solution customers keep renewing. Because some scenarios touch regulated domains, treat this article as educational—not legal or medical advice—and engage qualified professionals when needed.
At a glance, here’s a compact “fit guide” to help you aim quickly:
| Use case | Primary buyer | Core KPI | Typical time-to-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote assistance | Service/operations lead | First-time fix rate | Weeks |
| Training & simulation | L&D/clinical/HSSE lead | Time-to-competence | Weeks–months |
| Digital-twin reviews | Engineering/program lead | Design cycle time | Weeks |
| Warehouse work-instr. | Manufacturing/logistics lead | Throughput, errors | Weeks |
| BIM-to-field | Project/construction lead | Rework reduction | Weeks–months |
A fast path to traction: pick one play, instrument a baseline, and run a pilot with explicit exit criteria. In practice, the winning motion is: define the job to be done → pick a headset or handheld funnel that users already tolerate → build for five tasks, not fifty → measure change against one operational KPI → price against the cost of the current pain → expand by adjacent tasks.
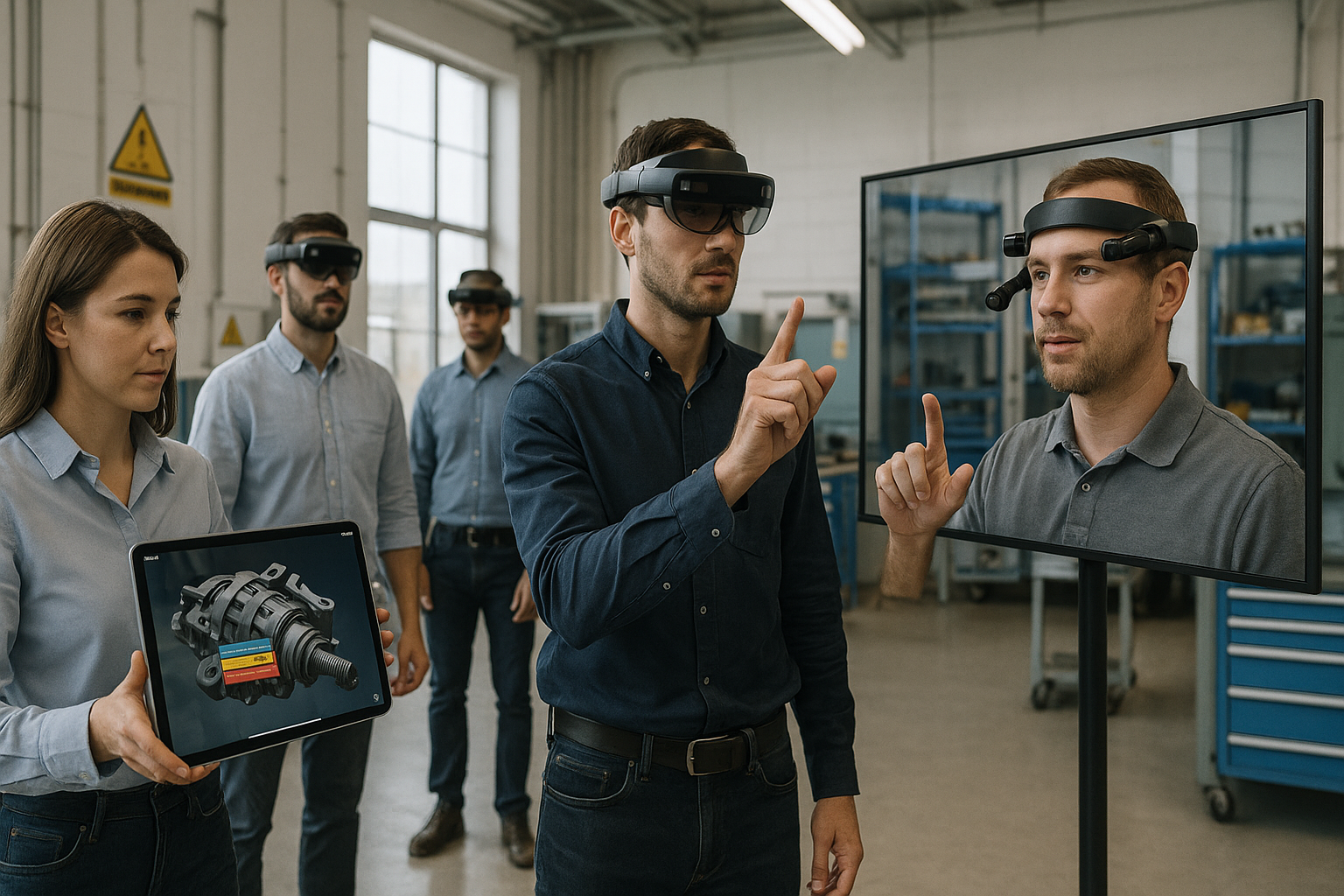
1. Remote Assistance for Field Service & Operations
Remote assistance is the lowest-friction AR entry point because it upgrades an existing workflow: “expert on a call.” The value proposition is straightforward—technicians stream what they see; experts annotate the live view; and both reduce truck rolls, cut mean time to repair, and improve first-time fix. You’re replacing static PDFs and phone descriptions with shared visual context that eliminates ambiguity at the moment of work. This play resonates in HVAC, industrial equipment, healthcare biomedical engineering, utilities, and any site with specialized assets. Buyers look for rapid deployment, SSO, role-based access, and tight audit trails. Lead with hands-free headsets where PPE allows, or use phones/tablets when headwear is impractical. Success stories often start with a single region or asset class and expand once metrics move.
How to do it
- Map the top 10 incident types by frequency × cost; pick the top 3 for pilot scripts.
- Integrate identity (IdP), ticketing (ServiceNow, Salesforce), and asset registry (EAM/CMMS).
- Provide offline capture with automatic sync for low-connectivity sites.
- Add on-video arrows, shape anchors, and freeze-frame markup; store recordings for QA.
- Train “expert coaches” to standardize guidance and escalate to engineering when needed.
- Offer a browser join link so customers or subcontractors can participate with zero installs.
Numbers & guardrails
- Target deltas: +10–20% first-time fix, −15–30% MTTR, −20–40% travel costs per incident.
- Ergonomics: ensure devices fit with safety helmets/eyewear; verify compliance to local PPE standards (e.g., ANSI/ISEA classes for helmets) and site rules.
- Privacy: log consent when capturing customer environments; mask sensitive dashboards during screen share.
Close by instrumenting a simple scorecard and reviewing monthly; when three consecutive months show sustained gains, expand to additional regions or asset types and bake the play into onboarding.
2. Training & Simulation for High-Risk or High-Variability Tasks
VR shines when real-world practice is risky, expensive, or rare. Immersive simulations let learners repeat procedures until competent, without consuming physical materials or blocking live equipment. Think confined-space entries, sterile technique, electrical lockout/tagout, or aircraft pushback choreography. The win is time-to-competence and error reduction, not “wow factor.” Effective programs pair scenario realism with objective scoring and remediation paths. For skill transfer to stick, practice sequences must mirror the real task, and muscle memory needs the same timing, reach, and decision tree you’ll face on the job.
How to do it
- Co-design with SMEs to capture “golden path” steps and the top 5 failure modes.
- Add formative feedback: slow-motion replays, heatmaps of gaze/errors, and on-the-spot hints.
- Integrate LMS/LRS (SCORM/xAPI) so completions, scores, and attempt histories feed compliance.
- Provide accessibility modes: seated options, reduced motion, adjustable haptics/audio.
- Keep scenarios short (8–15 minutes) and modular; chain them into a progressive pathway.
Numbers & guardrails
- Targets: aim for measurable gains like −25–40% critical errors in the first month of deployment, or −20–30% instructor hours per learner for standard procedures.
- Content cost: budget realistic ranges per scenario depending on fidelity and branching; keep assets reusable across variants.
- Safety: include pre-use checks and spotters for users prone to motion sickness; for clinical skills, validate content with appropriate governance boards.
Wrap with post-training job performance checks; when on-the-job defects drop and ramp time shortens, you have the evidence to expand to adjacent procedures and additional cohorts.
3. Digital-Twin Design Reviews & Collaborative Engineering
Spatial reviews compress what used to require printouts, exports, and multi-week meetings. Engineers, program managers, and suppliers meet around the same 1:1 model, overlay real-world constraints, and annotate decisions in context. The payoff is shorter design cycles, fewer late-stage changes, and clearer supplier handoffs. A “digital twin” here is a live, data-fed model of an asset and its processes; even a modest twin that syncs geometry, metadata, and status can unlock huge coordination gains. Your product should make loading complex assemblies boringly reliable, support materials/physics simplifications for headsets, and persist comments back to PLM issue trackers.
Tools/Examples
- Import from CAD/PLM (STEP, JT, glTF); preserve part hierarchies, materials, and metadata.
- Simplify heavy meshes (LODs, occlusion culling) and stream deltas rather than monolithic files.
- Pin annotations to parts; sync to Jira/Azure DevOps for traceability.
- Provide “what-if” toggles: swapped components, clearance overlays, and clash detection.
- Enable supplier “view-only” access with watermarks and expiration.
Numbers & guardrails
- Targets: −15–25% design review time per sprint, −20–35% late-stage rework items, and shortened supplier question/answer cycles.
- Data governance: segment models by supplier; encrypt at rest/in transit; align to your customer’s infosec requirements (ISMS/least-privilege, secure logging).
- Change management: teach a canonical naming/annotation convention to avoid messy backlogs.
Conclude by logging cycle-time wins and rework avoided; that makes the case to embed spatial reviews as a standard phase gate across programs.
4. Hands-Free Work Instructions on the Line or in the Warehouse
AR overlays step-by-step instructions, torque specs, and checks directly in a worker’s view. In assembly, kitting, and picking, this reduces cognitive load, cuts paper, and improves consistency—especially for seasonal or temp staff. The best products avoid over-engineering; they deliver a minimal, responsive HUD that supports scanning, confirmation, and quick help without breaking flow. Tie it to your customer’s MES/WMS so status updates and exceptions synchronize with existing dashboards.
How to do it
- Start with the “golden three” tasks that are high volume and painful: e.g., bin picking with many look-alikes, torque sequences with QA capture, or kit verification.
- Provide offline fallbacks for metal-heavy or RF-unfriendly facilities.
- Support voice and simple gaze or ring-scanner inputs; avoid tiny UI targets.
- Auto-capture evidence (photos/short clips) for audits and learning.
- Use progressive disclosure: only show what the operator needs at this step.
Numbers & guardrails
- Targets: +5–15% throughput on repetitive tasks, −30–50% picking errors on look-alike SKUs, −20–35% onboarding time for new hires.
- Ergonomics: ensure headsets work with safety helmets and prescription lenses; offer tablet/phone modes where headgear isn’t allowed.
- Privacy & labor: keep per-user metrics focused on training needs and safety outcomes; avoid “always on” monitoring without clear policy and consent.
End with a Kaizen-style review; when one line’s stats hold for two cycles, duplicate the flow to similar tasks and standardize your content model.
5. Healthcare: Pre-Op Planning, Patient Education, and Care Team Alignment
In care settings, spatial tools help teams visualize anatomy, plan surgical approaches, and explain options to patients more clearly. The practical wins are fewer surprises in the OR, more aligned expectations, and better informed consent. Beyond pre-op reviews, VR education can demystify procedures and post-op recovery, improving adherence and lowering anxiety. Products that fit here integrate with imaging (DICOM), support segmentation, and enable shared sessions across clinics. Keep language simple; when people are stressed, cognitive load spikes.
How to do it
- Convert imaging into 3D segments; preset transparency and clip planes for quick exploration.
- Offer shared sessions so radiology, surgery, nursing, and patients can see the same model.
- Capture snapshots to the record with clinician notes; keep PHI governed by the provider’s policies.
- Provide non-immersive “viewer” modes for patients and family on common devices.
- Localize content; health literacy varies widely.
Numbers & guardrails
- Targets: shorter case conferences, improved patient understanding scores, reduction in pre-op planning time, and fewer same-day reschedules.
- Regulatory: treat any clinical decision support claims carefully; when your product influences diagnosis or treatment, expect medical device regulations, validation, and appropriate quality systems.
- Safety: design for infection control; headset covers, cleanable materials, and quick wipe-downs matter.
Synthesize results by pairing operational metrics with patient-reported outcomes; that dual lens helps champions justify renewals and broader rollouts.
6. Construction & BIM-to-Field: Catching Clashes Before Concrete Sets
Construction margins are thin and rework is punishing. AR that aligns BIM models with the jobsite helps crews verify layout, detect clashes, and plan sequences without poring over 2D sheets in the wind. The play is to bring high-value model slices (MEP runs, penetrations, structural steel) to the point of work, not to “put the entire building in the headset.” Winning products make model alignment fast, resilient to drift, and share findings back to project management tools.
How to do it
- Pre-slice models by trade; include tolerances and color coding for “go/no-go.”
- Align using marker-based or spatial anchors, then lock to site control points.
- Enable quick captures: “pin issue,” auto-attach photos and coordinates, sync to RFIs.
- Provide tablet fallback; cranes and PPE don’t always mix with headsets.
- Train foremen in five-minute bursts at the trailer—keep it practical and repeatable.
Numbers & guardrails
- Targets: −15–25% rework on targeted scopes, fewer RFIs, and faster sign-offs for hold points.
- Safety: confirm compatibility with helmets, eyewear, and fall-protection gear; ensure the display doesn’t obscure line of sight where spotters are needed.
- Data: strip non-essential layers; heavy models tank performance and frustrate crews.
Tie outcomes to the cost of rework avoided; that framing converts site wins into budgeted line items for your expansion phases.
7. Retail Ops: Try-On, Planogram Compliance, and Store Execution
Beyond flashy try-on demos, the quiet value in retail is execution—are shelves correct, promos live, and displays where they should be? AR that guides associates through prioritized tasks, verifies planograms with visual AI, and previews fixtures in situ can lift conversion and cut compliance churn. For shoppers, low-friction try-ons reduce uncertainty, but ensure you measure the downstream impact on returns and swaps rather than vanity usage.
How to do it
- Combine computer vision with AR overlays to flag deviations and suggest fixes.
- Pre-configure store templates; avoid manual setup at the branch level.
- Log dwell time and associate touches to improve sequencing, not to micromanage.
- Provide private-mode try-ons with immediate side-by-side comparisons and share links.
- Integrate to POS/OMS so promos and stock states are accurate in overlays.
Numbers & guardrails
- Targets: −20–40% time to verify planograms, +2–5% conversion on assisted categories, measurable dip in return rates for fit-sensitive items.
- Privacy: keep all face/body data ephemeral; obtain explicit consent for any captures; allow opt-out with full functionality.
- Accessibility: include non-AR flows for low-vision customers; ensure store lighting and floor reflectivity don’t break tracking.
Synthesize learnings by correlating store-level execution with sales lift; when the linkage is clear, the chain will fund broader rollout and push for HQ integration.
8. Spatial Analytics: Seeing Complex Data Where Work Happens
Spatial computing can make dense dashboards tangible. Imagine plant KPIs hovering near lines, IoT anomalies pulsing on the asset, and flow bottlenecks mapped across a floor. The point isn’t novelty; it’s faster sense-making for operators who can’t leave the line for a screen. Your product should link to time-series sources, alarm systems, and role-based views so individuals see what they can act on without extra clicks.
How to do it
- Mirror existing dashboard logic; don’t invent new definitions of downtime or OEE.
- Add proximity logic: only show overlays when a user approaches a relevant zone.
- Support “drill-in” to recent alarms with one tap and keep a breadcrumb to exit quickly.
- Offer silent modes for noise-restricted areas and vibration cues where allowed.
- Log which overlays get used to prune and refine over time.
Numbers & guardrails
- Targets: shorter time-to-detect and time-to-act on alarms, fewer missed thresholds, better shift handover clarity.
- Infosec: treat operational data with the same controls as SCADA/OT views; harden local caches and apply least-privilege access.
- Human factors: avoid clutter; anchor information at natural decision points.
Close the loop by comparing alarm response metrics pre/post; publish a one-page win story for the next plant or region to adopt.
9. Sales Enablement for Complex, High-Consideration Products
If your customer sells large or configurable equipment, spatial demos help prospects understand scale, options, and trade-offs without a warehouse visit. AR on a tablet can place a life-size compressor in a plant bay; VR can simulate operating conditions and maintenance clearance. The objection you’re solving is uncertainty—“Will this fit? Can our team service it? Is the noise acceptable?” Equip reps and partners with portable, offline-capable demos tied to CRM so usage translates to pipeline insights.
How to do it
- Build a configurator that toggles options, materials, and clearances with one tap.
- Include a “fit checker” that flags doorway and platform conflicts automatically.
- Package a standard discovery flow and objection-handling cues into the app.
- Record sessions with customer permission; generate a spec snapshot for follow-up.
- Provide a “self-serve” link for stakeholders who weren’t in the room.
Mini case (example numbers)
A capital-equipment vendor runs 60 on-site demos per quarter with average travel cost of 400 per demo and a 22% conversion rate. Switching to mixed in-person and virtual demos yields 90 sessions per quarter, travel per demo drops to 140 on average, and conversion nudges to 25%. The change nets more touches, lower cost per opportunity, and a tangible pipeline lift without increasing headcount.
Conclude by connecting demo engagement to opportunity velocity; when sellers see faster cycles and fewer technical surprises, they’ll push to standardize your tool.
10. Accessibility, Rehabilitation, and Assistive Workflows
AR/VR can reduce barriers for workers and learners with sensory, cognitive, or mobility differences. Examples include simplified UIs with larger affordances, gaze-based dwell selections for hands-limited users, and VR rehab protocols that gamify repetitive exercises. The key is to augment, not overwhelm—design for clarity, fine control over motion, and gradual progressions. In enterprise contexts, pair assistive modes with manager tooling that tracks goals while respecting privacy.
How to do it
- Offer presets for high-contrast, reduced motion, and audio descriptions.
- Provide “guided mode” that paces steps with adjustable dwell and confirmation.
- Keep sessions short and positive-feedback heavy; track streaks and milestones.
- Export progress to the org’s learning or wellness systems with user consent.
- Build opt-in communities where users share tips and calibrations.
Numbers & guardrails
- Targets: improved task completion rates in assistive mode, better adherence to rehab exercises, and reduced support tickets for accessibility needs.
- Clinical caution: when positioning as rehab, involve qualified clinicians and adhere to appropriate device classifications and evaluation practices.
- Data ethics: minimize collection; give users transparent controls over what’s shared and with whom.
Wrap by celebrating independent wins—when individuals hit goals, adoption spreads and your product becomes part of inclusive workplace design rather than a bolt-on.
11. Safety, Compliance, and Inspections—From Checklist to Insight
Inspections tend to be repetitive and error-prone when done on paper. AR can transform them into guided, evidence-rich workflows with location-aware checklists, annotated captures, and automatic report generation. Think confined-space permits, ladder inspections, emergency equipment checks, and GMP compliance in cleanrooms. The trick is to map your flows to existing standards and make the record airtight so audits become routine rather than stressful.
How to do it
- Convert legacy checklists into step-locked tasks with required photo or video evidence.
- Use geofencing or markers so the correct inspection appears in the correct location.
- Auto-generate timestamped reports with issue severity and remediation owners.
- Provide escalation for critical findings and track closure SLAs in the same system.
- Train supervisors to review samples weekly and coach for consistency.
Numbers & guardrails
- Targets: higher on-time inspection completion, fewer repeat issues, and reduced audit findings.
- Standards alignment: map each task to the organization’s safety or quality framework; ensure the hardware integrates with required PPE and doesn’t obstruct situational awareness.
- Change mgmt: start with one facility; publish a short before/after reel to win peers.
Synthesize by turning checklists into a feedback loop; when insights drive fewer incidents, you’ve upgraded compliance from a cost center to a performance lever.
12. Visitor Experiences & Wayfinding for Campuses and Venues
Beyond flashy exhibits, the durable value in public spaces is wayfinding that reduces confusion and improves throughput. AR can guide visitors along accessible routes, highlight safety information, and personalize recommendations. In museums and corporate experience centers, spatial storytelling deepens engagement while capturing opt-in analytics that help curators iterate. Your product should gracefully degrade on older phones and work in crowded RF environments.
How to do it
- Offer clear, floor-aware navigation with step-by-step AR arrows and 2D fallback.
- Build content blocks curators can update without developer help.
- Provide “quiet mode” routes and accessibility filters for elevators or ramps.
- Batch download assets per floor to survive spotty connectivity.
- Respect privacy: keep paths on-device unless users opt in to share.
Mini case (example numbers)
A venue with 30,000 weekly visitors sees 8% of guests ask staff for directions and 12% arrive late to timed entries. After deploying AR wayfinding with 2D backup, help-desk queries fall to 3% and late arrivals drop to 6%. The venue gains smoother flows, happier staff, and better throughput during peaks.
Tie results to staffing and guest satisfaction; when the numbers improve, the operations team becomes your long-term sponsor.
Conclusion
The AR/VR resurgence beyond gaming isn’t about novelty—it’s about compressing time, reducing errors, and aligning people around shared context. Startups win when they pick one workflow that bleeds money or creates risk, replace ambiguity with shared visual understanding, and measure the change in a KPI the buyer already reports. Keep hardware pragmatic (phones/tablets where headgear struggles; headsets where hands-free matters). Build the smallest slice that upgrades five common tasks; integrate with identity and the systems of record; and prove value with a scoreboard, not a sizzle reel. As you expand, codify your playbook: onboarding checklists, data-handling standards, and prebuilt integrations. That repeatability is the motor that turns pilots into programs and programs into platforms.
Ready to move? Pick one play, one KPI, and one pilot site—then ship a minimal flow your users love.
FAQs
1) What’s the fastest AR/VR play to pilot in a traditional enterprise?
Remote assistance is usually fastest because it wraps an existing workflow—experts already take calls—and devices can be phones or tablets. Define three incident types, script the calls, turn on recordings and markup, and integrate with the ticketing system. Make the success criterion simple: a sustained lift in first-time fix and a measurable cut in mean time to repair. With those deltas, you can justify further rollout and fund the next play.
2) How do I choose hardware without overcommitting?
Work backward from the task environment. If workers need both hands and wear PPE, test headsets that mount with helmet adapters; otherwise, start with tablets or phones that teams already carry. Validate comfort, battery life, and camera quality in the real environment, not the demo room. Maintain a dual-mode UI so the same workflow functions on head-worn and handheld form factors, which protects you from device availability swings and keeps training simple.
3) What KPIs should I track first?
Pick one operational metric tied to money or risk for each play: first-time fix, mean time to repair, rework rate, time-to-competence, planogram compliance time, or alarm response time. Establish a clear baseline for two to four weeks, run the pilot, and report the delta with confidence intervals where you can. Avoid vanity metrics like headset hours without tying them to outcomes; they rarely move budget holders.
4) How do I price an AR/VR solution fairly?
Price against the cost of the current pain. For example, if each truck roll costs hundreds and you prevent dozens per quarter, your annual value is clear. Combine a platform fee with per-named or per-device pricing and discount for multi-site commitments. Include support, updates, and a content refresh cadence in writing so customers know what’s covered and when. Transparent pricing builds trust and shortens procurement cycles.
5) What’s the most common reason AR/VR pilots stall?
Scope creep and unclear exit criteria. Teams try to satisfy every stakeholder, end up with long lists of edge cases, and never reach a conclusion. Keep pilots narrow: one site, one workflow, one KPI. Define “done” in advance—e.g., improve first-time fix by a specific margin for three consecutive months—and commit to a “yes/no” rollout decision based on that scorecard. Publish a short internal case study so the next site can copy your setup.
6) How do I handle data privacy and security?
Minimize collection and expose controls to users. Avoid capturing faces or screens unless necessary and always log consent. Encrypt data in transit and at rest, apply least-privilege access, and integrate with the customer’s identity provider for SSO and audit trails. Where overlays show sensitive operational data, treat them as you would control-system dashboards with strict access policies and revocation procedures. Clear documentation of your data flows helps security reviews finish faster.
7) What about motion sickness and ergonomic concerns?
Design with humans in mind. Favor stable overlays, avoid rapid camera moves, provide seated and reduced-motion modes, and keep sessions short. For head-worn devices, ensure compatibility with safety helmets and eyewear, and validate comfort during real shifts. Offer non-immersive fallbacks so no one is excluded. User comfort surveys and quick opt-out controls show you respect the person, not just the task.
8) Where do I find the right early customers?
Look for teams with an urgent operational pain, a champion who owns the KPI, and a budget they control. Maintenance organizations with aging equipment, L&D leaders who must onboard seasonal staff, or construction teams facing schedule pressure are classic matches. Bring a concrete pilot plan and credible references. If you’re new, partner with a system integrator or equipment vendor to piggyback on their installed base and trust.
9) How do I keep content fresh without ballooning costs?
Standardize your content model and build templates for common steps, checklists, and validations. Reuse assets across scenarios and automate mesh simplification for spatial content. Maintain a quarterly refresh cadence with change logs and deprecations. Expose a lightweight content editor for customers’ power users so they can update labels, steps, and thresholds without waiting on your team. Track which content gets used and retire the rest.
10) What regulatory or standards issues should I watch?
Map your claims and contexts carefully. If your product influences clinical decisions, expect medical device regulations and validation. In industrial settings, ensure head-worn devices and accessories cooperate with PPE requirements and safety policies. When handling operational data, align with your customer’s security frameworks and documentation. The safest posture is to meet the customer where they already are—don’t invent new compliance categories.
References
- Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality in Medical Devices, U.S. Food & Drug Administration, publication date listed on page; https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/digital-health-center-excellence/augmented-reality-and-virtual-reality-medical-devices
- Designing for visionOS – Human Interface Guidelines, Apple Developer Documentation, includes guideline update dates; https://developer.apple.com/design/human-interface-guidelines/designing-for-visionos
- Mixed Reality Documentation (HoloLens and Windows Mixed Reality), Microsoft Learn, living documentation with revision history; https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/mixed-reality/
- ISO 9241-391: Ergonomics of human-system interaction — Requirements for image content to reduce photosensitive seizure risk, International Organization for Standardization, publication info on standard page; https://www.iso.org/standard/56350.html
- Augmented Reality (AR) Usability Evaluation Framework: A Case of Public Safety Communications, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), report publication information on page; https://www.nist.gov/publications/augmented-reality-ar-usability-evaluation-framework-case-public-safety-communications
- The metaverse: how to safely integrate new visualisation technologies at work, European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (EU-OSHA), article publication date on page; https://osha.europa.eu/en/highlights/metaverse-how-safely-integrate-new-visualisation-technologies-workplace
- Definition of a Digital Twin, Digital Twin Consortium, publication date on site; https://www.digitaltwinconsortium.org/initiatives/the-definition-of-a-digital-twin/
- BID Group Improves Service and CX With Vuforia Chalk, PTC Case Study, publication details on page; https://www.ptc.com/en/case-studies/bid-group-streamlines-service-with-vuforia-chalk
- Virtual reality for stroke rehabilitation (Plain-language summary), Cochrane, article page includes publication date; https://www.cochrane.org/evidence/CD008349_virtual-reality-stroke-rehabilitation
- 29 CFR 1910.135 – Head Protection, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), regulatory page with revision history; https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1910/1910.135