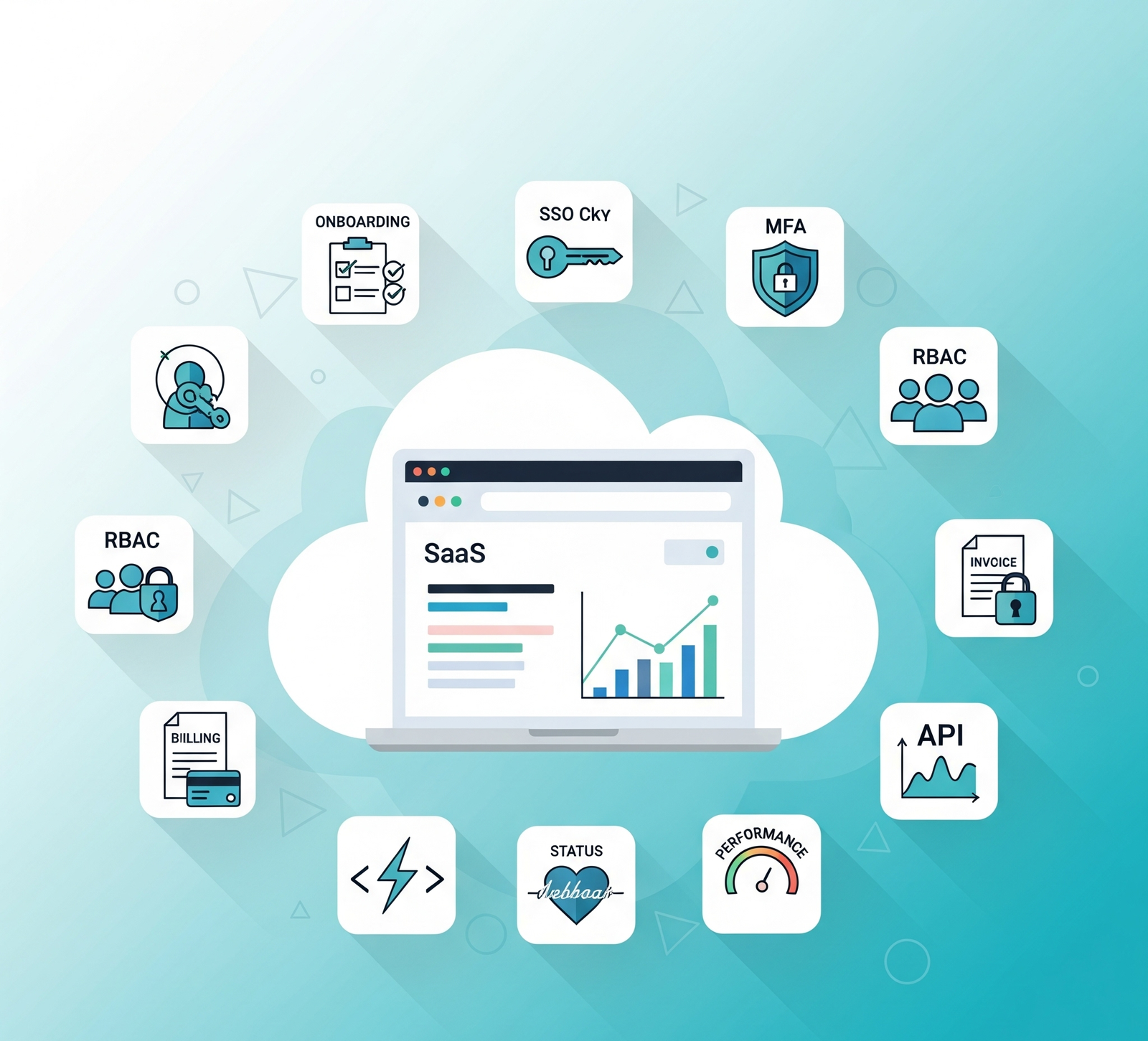
Building a successful SaaS product isn’t just about writing great code—it’s about creating a system that sells itself, secures itself, scales by design, and keeps customers coming back. In this guide, you’ll learn the 10 must-have features every serious SaaS product should prioritize, how to implement each one (step-by-step), what to measure, and the common pitfalls to avoid. If you lead a product team, run a startup, or own a roadmap for a cloud product, this is for you. By the end, you’ll have a practical 4-week starter plan and a checklist you can adopt today.
Key takeaways
- Onboarding that activates value fast beats long feature lists.
- Identity and access (SSO, MFA, RBAC) is table stakes and must be friction-aware.
- Privacy, security, and observability are product features, not IT chores.
- API-first, integration-ready design future-proofs your ecosystem.
- In-product analytics and feedback loops drive retention and roadmap clarity.
- Performance and accessibility directly shape adoption and expansion.
1) Frictionless Onboarding & Self-Serve Activation
What it is & why it matters
Onboarding is the path from “curious” to “confident.” It bundles sign-up, first-run experiences, guided tours, templates, and an in-app checklist that helps new users reach their first moment of value quickly. Great onboarding reduces time-to-value (TTV), cuts support load, and lifts activation and trial-to-paid conversion.
Prerequisites & low-cost alternatives
- Skills: Product design, UX writing, customer research, event tracking.
- Tools: In-app guide/tooltip system, email automation, product analytics.
- Low cost: Start with a single “welcome modal” + 3-step checklist and one “golden path” template.
Step-by-step implementation
- Define the “aha”: One clear, observable action that demonstrates core value (e.g., “import a file,” “invite a teammate,” “publish a report”).
- Map the first session: Remove nonessential fields from sign-up. Use progressive profiling later.
- Build a 3–5 step checklist that points to the aha and celebrates completion.
- Seed templates/samples so users don’t start from a blank screen.
- Trigger lifecycle emails for stalled users (e.g., 24h, 72h, 7d).
- Instrument events for sign-up, first session, aha, invite, and paywall views.
- Run an A/B test: Checklist vs. no checklist. Keep what lifts activation.
Beginner modifications & progressions
- Start with one segment (e.g., single-seat admins), then expand to teams and enterprise.
- Add contextual tooltips only after you’ve simplified screens.
- Later, personalize onboarding by role/industry and adapt steps based on detected friction.
Recommended frequency/metrics
- Review weekly: Activation rate, TTV, “aha” completion, invite rate, trial-to-paid conversion.
- Monthly: Cohort retention (e.g., Week 1, Week 4), support tickets from new users.
Safety, caveats, common mistakes
- Don’t overwhelm with long tours.
- Don’t gate the aha behind lengthy setup.
- Avoid asking for payment before value is visible (unless a clear enterprise motion requires it).
Mini-plan example
- Day 1: Reduce sign-up fields to email + password or SSO.
- Day 3: Launch a 3-step checklist leading to the aha and one celebratory success state.
2) Authentication & MFA That Don’t Get in the Way (SSO Included)
What it is & why it matters
Authentication verifies identity; MFA adds a second factor; SSO lets users sign in via providers like Google or enterprise identity platforms. These reduce account takeovers and IT friction, and they’re expected by security-conscious buyers.
Prerequisites & low-cost alternatives
- Skills: Backend engineering, security best practices, identity protocols.
- Tools: OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect for consumer SSO; SAML/OIDC for enterprise.
- Low cost: Start with email + password + TOTP MFA; add Google/Microsoft SSO; add SAML for enterprise when needed.
Step-by-step implementation
- Choose your IdP flows: OIDC for modern clouds; SAML for legacy/enterprise.
- Implement MFA: TOTP authenticator first; later add WebAuthn/passkeys.
- Secure password flows: Hash with a strong algorithm; rate-limit and monitor.
- Session hygiene: Short tokens, refresh securely, detect anomalies.
- Admin controls: Enforce MFA, view sign-in logs, set session policies.
- Document it: Clear SSO/MFA setup guides for admins.
Beginner modifications & progressions
- Start with OIDC social SSO; add SAML and SCIM user provisioning for enterprise later.
- Offer magic links for low-friction trials; enforce MFA for paid orgs.
Recommended frequency/metrics
- Weekly: MFA adoption, password reset rate, failed logins, account lockouts.
- Monthly: Authentication-related ticket volume, SSO adoption among eligible orgs.
Safety, caveats, common mistakes
- Don’t store plaintext secrets.
- Don’t ship without rate limiting and brute-force protections.
- Avoid unclear error messages—balance security with usability.
Mini-plan example
- Sprint 1: Add TOTP MFA + Google OIDC.
- Sprint 2: Add SAML for enterprise + audit sign-in report.
3) Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) & Granular Permissions
What it is & why it matters
RBAC assigns permissions to roles (e.g., Admin, Billing, Viewer) and roles to users or groups. It’s essential for team collaboration, least-privilege access, and enterprise deals.
Prerequisites & low-cost alternatives
- Skills: Authorization modeling, backend policy enforcement, UX for permissions.
- Tools: Policy engine or database-backed ACLs; directory syncing (SCIM) later.
- Low cost: Start with three roles and a simple policy matrix.
Step-by-step implementation
- Define resources & actions: e.g., Projects (read/write/share/delete), Billing (view/manage).
- Create a role matrix: Map each role to allowed actions clearly.
- Enforce on the backend: Never rely on UI only. Add tests for critical paths.
- Build role management UI: Assign roles at org/project levels.
- Log authorization events: Denies, escalations, role changes.
Beginner modifications & progressions
- Begin with coarse roles; add custom roles and resource-level scopes later.
- For large orgs, add group/SCIM support and approver workflows.
Recommended frequency/metrics
- Monthly: Requests denied due to permissions, time to grant access, number of custom roles used.
- Security review: Quarterly role audits.
Safety, caveats, common mistakes
- Don’t hardcode permissions in multiple places—use a single policy layer.
- Avoid silent failures; show clear “need permission” states with request flows.
Mini-plan example
- Week 1: Admin, Member, Viewer roles + backend checks.
- Week 3: Project-level overrides + audit trail for role changes.
4) Privacy-by-Design, Security Controls & Compliance Readiness
What it is & why it matters
Customers expect privacy choices, robust encryption, and audit trails. For many markets, readiness for frameworks (e.g., data-protection regulations or industry standards) is a sales blocker or accelerator. Treat these as first-class product features.
Prerequisites & low-cost alternatives
- Skills: Security engineering, threat modeling, data mapping.
- Tools: At-rest and in-transit encryption, key rotation, audit logging.
- Low cost: Start with encryption defaults, a data map, and transparent privacy settings.
Step-by-step implementation
- Data inventory & flows: What you collect, why, where it goes, who accesses it.
- Build user controls: Download/export, delete, consent toggles, data retention settings.
- Audit logging: Record significant events (login, role changes, data exports).
- Security baseline: Strong cryptography, secure secrets management, vulnerability scanning.
- Docs & DPA: Explain practices clearly; provide a standard data processing addendum for customers.
Beginner modifications & progressions
- Start with core controls; later add regional hosting, advanced retention policies, and finer consent categories.
- Offer privacy requests self-serve; automate status tracking.
Recommended frequency/metrics
- Monthly: Audit log review coverage, time to close high-severity findings, privacy request SLA.
- Quarterly: Pen-test / vulnerability remediation review.
Safety, caveats, common mistakes
- Don’t promise compliance you haven’t achieved.
- Don’t bury privacy controls; make them discoverable and understandable.
- Keep audit logs tamper-resistant and access-controlled.
Mini-plan example
- This month: Add CSV/JSON export + delete-account flows + audit log view for admins.
- Next month: Add region data residency option for eligible tiers.
5) Billing, Subscriptions & Pricing That Fit How Customers Buy
What it is & why it matters
SaaS monetization needs flexible pricing (per-seat, usage-based, or hybrid), trials, invoicing for finance teams, proration, and dunning. Self-serve revenue is fuel for efficient growth; clean finance data reduces churn and disputes.
Prerequisites & low-cost alternatives
- Skills: Payments integration, subscription logic, revenue recognition basics.
- Tools: Payment processor, billing system, tax handling.
- Low cost: Start with a single plan + free trial + receipts; expand to metered add-ons later.
Step-by-step implementation
- Define packaging: Map features to tiers; keep it simple initially.
- Implement checkout: PCI-aware processor, secure tokenization, receipts.
- Subscription logic: Trials, upgrades/downgrades, proration, refunds.
- Dunning: Retry logic, email nudges, grace periods.
- Admin portal: Update payment method, invoices, usage views.
Beginner modifications & progressions
- Start with seat-based pricing; add usage-based components once you have stable metering.
- Add annual prepay discounts and invoicing for larger accounts.
Recommended frequency/metrics
- Weekly: Conversion to paid, involuntary churn (payment failures), time to resolve billing tickets.
- Monthly: Expansion revenue, average revenue per account, trial conversion.
Safety, caveats, common mistakes
- Don’t hide pricing or overcomplicate tiers.
- Avoid manual billing spreadsheets—errors cause churn.
- Document VAT/tax handling and invoices clearly.
Mini-plan example
- Sprint 1: Free trial + card checkout + email receipts.
- Sprint 2: Dunning + in-app upgrade prompts + plan change proration.
6) API-First Platform, Webhooks & SDKs
What it is & why it matters
An API-first product treats the API as a first-class surface with stable contracts, clear errors, and versioning. Webhooks push events; SDKs accelerate adoption. This unlocks integrations, automation, and ecosystems.
Prerequisites & low-cost alternatives
- Skills: API design, documentation, security, versioning.
- Tools: Specification (e.g., OpenAPI), developer portal, sandbox keys.
- Low cost: Start with a read-only API for core objects and one webhook (e.g., “account.updated”).
Step-by-step implementation
- Define resources & verbs: Follow consistent naming, pagination, filtering.
- Write a spec: Use a formal interface description; generate reference docs.
- Standardize errors: Adopt a structured error format with machine-readable fields.
- Auth: Token-based with scopes; rotate keys; provide test mode.
- Webhooks: Signed payloads, retries with exponential backoff, replay protection.
- Versioning: Date-based or semantic; deprecation policy with migration guides.
- DX polish: Quickstarts, curl examples, minimal SDKs for popular languages.
Beginner modifications & progressions
- Start with GET endpoints and add POST/PUT/PATCH gradually.
- Release clients for two languages; expand based on usage.
Recommended frequency/metrics
- Weekly: API error rate, P95 latency, webhook retry volume, time to first successful call.
- Quarterly: Percentage of customers using API or webhooks, SDK install counts.
Safety, caveats, common mistakes
- Don’t break existing clients; honor deprecation windows.
- Don’t ship webhooks without signature verification.
- Avoid undocumented fields; “beta” features belong behind flags.
Mini-plan example
- This week: Document core resources + publish spec + issue API keys in dashboard.
- Next: Add signed webhooks for “invoice.paid” and “user.invited.”
7) Reliability, Observability & a Real Status Page
What it is & why it matters
Reliability means your product does what it should, when it should. Observability lets you detect, understand, and fix issues—fast. A public status page and incident comms build trust.
Prerequisites & low-cost alternatives
- Skills: Monitoring, alerting, incident response.
- Tools: Logging, tracing, metrics, uptime checks, runbooks.
- Low cost: Start with basic uptime checks + error tracking + manual status updates.
Step-by-step implementation
- Define SLIs/SLOs: Pick user-centric reliability signals (e.g., successful logins, API 2xx rate).
- Instrument telemetry: Collect logs, metrics, and traces across services.
- Dashboards & alerts: On-call rotation, paging thresholds, and runbooks.
- Status page: Show component health; post incident timelines and RCA summaries.
- Game days: Practice failure scenarios.
Beginner modifications & progressions
- Start with availability and latency; add error budgets to balance shipping vs. fixing.
- Add synthetic checks for core workflows.
Recommended frequency/metrics
- Continuous: SLI compliance vs. SLO targets; alert fatigue; mean time to resolve (MTTR).
- Post-incident: Root cause themes, time to notify customers, time to mitigate.
Safety, caveats, common mistakes
- Don’t alert on noise; calibrate thresholds.
- Avoid hidden incidents—communicate early and clearly.
- Don’t over-collect logs without retention policies.
Mini-plan example
- Week 1: Publish a status page + instrument uptime probe for login and API.
- Week 3: Add distributed tracing for top 3 backend calls.
8) In-Product Analytics & Feedback Loops (NPS, Surveys, and More)
What it is & why it matters
To improve what users actually use, you need product analytics (events, funnels, retention, cohorts) and a steady loop of qualitative feedback (NPS, in-app surveys, interviews). This informs roadmap, pricing, and onboarding.
Prerequisites & low-cost alternatives
- Skills: Event modeling, experimentation, user research.
- Tools: Product analytics, survey tooling, session replay (optional).
- Low cost: Track 10–15 core events, run one NPS touchpoint per quarter, and add a single “Was this helpful?” survey in a key flow.
Step-by-step implementation
- Define your event taxonomy: Sign Up, Project Created, Invite Sent, Export Downloaded, etc.
- Instrument client + server: Ensure consistency and de-dupe.
- Build core dashboards: Activation funnel, weekly retention, feature adoption.
- Launch NPS + micro-surveys: Keep it short; rotate prompts.
- Close the loop: Respond to detractors; tag feedback by theme; align roadmap.
Beginner modifications & progressions
- Start with snapshot metrics; evolve to cohort analysis and experiments.
- Add user interviews for high-value segments.
Recommended frequency/metrics
- Weekly: Activation, feature adoption, DAU/WAU/MAU ratios.
- Monthly: NPS trend, survey response rate, top friction themes.
Safety, caveats, common mistakes
- Don’t log sensitive data accidentally.
- Avoid vanity metrics; focus on behaviors linked to retention and revenue.
- Don’t spam surveys—respect attention.
Mini-plan example
- This week: Track 12 core events, create an activation funnel, add a 1-question survey.
- Next month: Add quarterly NPS and detractor follow-up workflow.
9) Integrations, Imports/Exports & a Growing Ecosystem
What it is & why it matters
Your product lives in a stack. Integrations (e.g., identity, data sources, comms, payments), bulk import/export, and a marketplace (even a lightweight one) reduce switching costs and enable stickier workflows.
Prerequisites & low-cost alternatives
- Skills: Partner APIs, data mapping, ETL basics, OAuth scopes.
- Tools: Integration framework, secrets vault, transformation layer.
- Low cost: Start with a CSV import/export and 2–3 high-impact integrations.
Step-by-step implementation
- Prioritize top connections: Poll customers; pick the top 3 to start.
- Implement secure OAuth flows and scoped tokens; handle webhooks from partners.
- Build importers/exporters with schema validation and progress UI.
- Create integration cards with setup guides and test buttons.
- Partner with vendors for co-marketing and certification where it matters.
Beginner modifications & progressions
- Begin with unidirectional sync; add bidirectional sync and conflict resolution later.
- Offer a lightweight marketplace or catalog page as inventory grows.
Recommended frequency/metrics
- Monthly: Integration adoption per customer, import success rate, % of active customers using at least one integration.
- Quarterly: Partner-sourced leads/revenue.
Safety, caveats, common mistakes
- Don’t store partner tokens insecurely.
- Avoid brittle scrapers—favor official APIs and backoff policies.
- Document limits and error handling clearly.
Mini-plan example
- Month 1: CSV import/export + two native integrations.
- Month 2: Add webhooks and an “integrations gallery” page.
10) Performance, Accessibility & Mobile-Ready UI
What it is & why it matters
Speed and clarity drive engagement. Accessibility broadens your audience and often improves usability for everyone. A responsive, mobile-friendly UI ensures your app works wherever work happens.
Prerequisites & low-cost alternatives
- Skills: Frontend performance, semantic HTML, responsive design, accessibility testing.
- Tools: Performance audits, accessibility checkers, design system tokens.
- Low cost: Start with semantic components, keyboard support, and a performance budget on critical paths.
Step-by-step implementation
- Set budgets: Establish thresholds for key performance metrics on core pages.
- Optimize critical paths: Code-split, lazy-load, prefetch, compress, and cache smartly.
- Accessibility passes: Focus, labels, contrast, landmarks, keyboard navigation, error messaging.
- Responsive design system: Grid, spacing, typography, component library with tokens.
- Mobile-first critical flows: Ensure top 3 workflows are smooth on small screens.
Beginner modifications & progressions
- Start with AA contrast and keyboard support; later add more advanced patterns, live regions, and complex form improvements.
- Introduce performance lab tests, then validate with real-user monitoring.
Recommended frequency/metrics
- Weekly: Page-level performance on core routes, error surfaces, and form completion time.
- Monthly: Accessibility issue count, assistive tech feedback, mobile conversion vs. desktop.
Safety, caveats, common mistakes
- Don’t ship inaccessible custom components; extend tested primitives.
- Avoid regressions—add automated performance and accessibility checks to CI.
- Don’t optimize assets while ignoring long-running API calls—end-to-end matters.
Mini-plan example
- Sprint 1: Audit top two pages; fix low-hanging performance wins; add keyboard navigation and focus states.
- Sprint 2: Establish CI checks for performance and accessibility thresholds.
Quick-Start Checklist (Use Today)
- Define a single, measurable “aha” moment and add a 3-step onboarding checklist.
- Enable MFA + one SSO option; log sign-ins and suspicious activity.
- Implement three core roles (Admin/Member/Viewer) and enforce on the backend.
- Ship data export, delete-account, and an audit log for admins.
- Offer a simple plan, clean checkout, proration, and dunning.
- Publish an API spec, one webhook, and two SDK quickstarts.
- Stand up a public status page; define two SLIs and one SLO per SLI.
- Track 10–15 core product events; launch one micro-survey or NPS pulse.
- Build two native integrations + CSV import/export.
- Run a performance & accessibility pass on your top two pages.
Troubleshooting & Common Pitfalls
- Onboarding flatlines: Your aha is too far away. Remove steps, pre-seed sample data, and reduce required fields.
- Support tickets spike after SSO: You’re mismatching emails to identity claims. Normalize and map attributes consistently.
- Permission confusion: Roles aren’t clear. Add tooltips, preview states, and request-access flows.
- Privacy requests stall: Centralize requests, automate verification, and add status tracking in-app.
- Involuntary churn: Tighten dunning, add multiple payment methods, and warn about card expiry.
- API adoption lags: Your docs are unclear. Add working examples, language SDKs, and a sandbox mode.
- Alert fatigue: Tune thresholds; route only user-impacting alerts to paging; everything else to inbox/slack.
- Analytics noise: Over-instrumenting. Curate an event taxonomy; deduplicate; keep names stable.
- Integration fragility: Lack of backoff/retries. Implement idempotency and exponential backoff.
- Accessibility regressions: Missing CI checks. Add automated tests + manual screen-reader passes for critical flows.
How to Measure Progress (What “Good” Looks Like)
- Activation: > X% of new sign-ups complete aha within 24–48 hours; TTV trending down.
- Security adoption: MFA enabled for Y% of users/orgs; SSO usage rises among eligible customers.
- Authorization health: Low permission-related tickets; < Z% denied requests on common tasks.
- Privacy & security hygiene: Time to fulfill data requests within your target SLA; high coverage for audit logs; critical vulnerabilities remediated promptly.
- Revenue operations: Trial-to-paid improves; involuntary churn decreases; billing tickets shrink.
- Developer ecosystem: Growing API calls from distinct accounts; webhook delivery success > 99%; SDK downloads climbing.
- Reliability: SLOs met; MTTR trending down; transparent incident comms.
- Product fit: Activation up, retention cohorts stabilizing, NPS improving, adoption of key features rising.
- Integrations: % of accounts with ≥1 integration increases month over month.
- UX quality: Faster key flows; fewer accessibility issues; better mobile completion rates.
A Simple 4-Week Starter Plan
Week 1: Activation & Safety Nets
- Ship a 3-step onboarding checklist to the aha.
- Enable MFA; add a sign-in audit log view.
- Track 12 core product events and build an activation dashboard.
Week 2: Monetization & Ecosystem Basics
- Launch a clear pricing page, trial, and clean checkout.
- Add CSV import/export and one high-demand integration.
- Publish your API spec and a signed webhook for one key event.
Week 3: Reliability & Insight
- Define two SLIs and SLOs; wire dashboards and alerts.
- Publish a status page and incident template.
- Launch a micro-survey in the “aha” flow; bucket feedback.
Week 4: Performance, Accessibility & RBAC
- Run a performance pass on top two pages; add CI checks.
- Fix keyboard navigation and contrast issues on key components.
- Enforce Admin/Member/Viewer roles in the backend and show permission-aware UI.
FAQs
1) What’s the best order to implement these features?
Start with activation (onboarding and aha), then identity (MFA/SSO) and basic RBAC. Next, lock in billing and a minimal API. Layer on observability, privacy controls, and integrations. Performance and accessibility are ongoing.
2) How much onboarding is “too much”?
If users can’t reach the aha in their first session without tutorial fatigue, it’s too much. Prefer a short checklist + seeded templates over long tours.
3) Do I need SSO from day one?
If you sell to SMB/consumer, start with OIDC social SSO and TOTP MFA. Add enterprise SSO (SAML/OIDC) when larger customers request it.
4) What’s a good minimal RBAC setup?
Admin (full control), Member (create/edit within assigned scope), Viewer (read-only). Expand to custom roles after you see real permission patterns.
5) How do I avoid “checkbox compliance”?
Expose real user controls (export/delete/consent), maintain audit logs, and be honest about your posture. Compliance should reflect genuine security and privacy practices.
6) Which pricing model should I choose?
If your value scales with seats, start seat-based. If value scales with usage (e.g., API calls, data processed), consider usage-based or hybrid. Keep it simple.
7) What’s the minimum API I should ship?
A documented, read-only set of core resources, a stable auth flow, clear error responses, and one webhook. Add write endpoints and SDKs as demand grows.
8) How do I pick the right SLOs?
Choose SLOs that reflect what users feel (e.g., success rate on key actions, latency under a threshold for core endpoints). Keep them few and meaningful.
9) How often should I run NPS?
Quarterly is a practical cadence. Follow up with detractors quickly; tag themes and route to owners.
10) What if I can’t build many native integrations?
Start with CSV import/export and a few strategic integrations. Provide webhooks, an API, and guides so partners or customers can build the rest.
11) How do I keep performance from regressing?
Add budgets and automated checks in CI/CD. When you ship a new feature, measure its impact on your top flows before release.
12) What’s the simplest way to get started on accessibility?
Use semantic HTML, ensure keyboard navigation works everywhere, meet contrast requirements, and provide clear error/help text. Then layer in more advanced patterns.
Conclusion
SaaS success comes from intentional foundations: fast activation, secure and sane identity, clean authorization, trust-building privacy and reliability, flexible monetization, a developer-friendly platform, and UI that puts speed and inclusivity first. You don’t need to ship everything at once—ship the smallest slice that makes the next win inevitable. Then stack those wins.
Copy-ready CTA: Start today: pick one feature above, ship the smallest valuable version this week, and measure the lift.
References
- “Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.2,” W3C, 2024, https://www.w3.org/TR/WCAG22/
- “WCAG 2 Overview,” W3C Web Accessibility Initiative, n.d., https://www.w3.org/WAI/standards-guidelines/wcag/
- “What’s New in WCAG 2.2,” W3C Web Accessibility Initiative, 2023, https://www.w3.org/WAI/standards-guidelines/wcag/new-in-22/
- “How to Meet WCAG (Quick Reference),” W3C, n.d., https://www.w3.org/WAI/WCAG22/quickref/
- “Core Web Vitals,” web.dev (Google), n.d., https://web.dev/explore/learn-core-web-vitals
- “Understanding Core Web Vitals and Google search results,” Google Developers, n.d., https://developers.google.com/search/docs/appearance/core-web-vitals
- “The Twelve-Factor App,” 12factor.net, n.d., https://12factor.net/
- “Site Reliability Engineering (SLI/SLO) concepts,” Google SRE (overview), n.d., https://sre.google/books/ (see concepts pages)
- “OpenAPI Specification,” Swagger / OpenAPI Initiative, n.d., https://swagger.io/specification/
- “OpenAPI-Specification (GitHub),” OpenAPI Initiative, 2024, https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification
- “RFC 9457: Problem Details for HTTP APIs,” IETF RFC Editor, 2023, https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc9457.html
- “RFC 7807: Problem Details for HTTP APIs,” IETF Datatracker (obsolete by RFC 9457), 2016, https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7807
- “What is OpenTelemetry?,” OpenTelemetry docs, 2025, https://opentelemetry.io/docs/what-is-opentelemetry/
- “OpenTelemetry Documentation,” OpenTelemetry, 2025, https://opentelemetry.io/docs/
- “SOC 2® — SOC for Service Organizations,” AICPA & CIMA, 2023–2025, https://www.aicpa-cima.com/topic/audit-assurance/audit-and-assurance-greater-than-soc-2